BIM 2025: The Quick Lowdown
- Data is King: BIM has grown up. It's no longer just about 3D models; the real muscle is in the rich, structured information embedded within every element.
- Smart Dimensions: 4D (scheduling) and 5D (cost) are where BIM truly shines, offering practical, integrated project controls. Anything beyond is mostly just adding more data layers – useful, but not a new "dimension."
- Integrated Platforms are Key: The future isn't about juggling standalone tools. True BIM enablement comes from platforms that understand and use BIM data holistically, from the first sketch to facility management.
BIM's Big Shift: From 3D Eye Candy to Data Powerhouse
Remember when BIM was mainly about knocking out impressive 3D visualizations? Those days are long gone. By 2025, Building Information Modeling has firmly cemented its role as a data-driven process, not just a modeling exercise. The initial buzz around 3D was just the gateway. The real revolution is in the "I" – the Information. This isn't about creating a static digital sculpture; it's about building an intelligent, data-rich digital counterpart of a physical asset.
The original vision for BIM was always grander than just replacing 2D drawings with 3D models. It was about visualizing *data* in a real-world, spatial context. Think of the 3D model as the intelligent container, but the gold is the structured data attached to every wall, window, pipe, and beam. This data isn't just descriptive; it's operative. It drives decisions, automates processes, and connects previously siloed stages of a project.
This evolution was fueled by a practical need. We, as industry pros, got tired of the disconnects. A beautiful model that didn't talk to the schedule or the budget? That's a recipe for headaches and lost money. Mandates, like the UK government's push for BIM on public projects starting way back, accelerated this shift. Now, in 2025, the focus is squarely on interoperability, open standards (like ISO 19650), and ensuring that data flows seamlessly between different tools and stakeholders. A window in a 2025 BIM model isn't just a geometric shape; it carries its fire rating, U-value, supplier details, cost code, and even installation instructions – all accessible and usable.
Getting Real with Dimensions: 4D & 5D Take Center Stage
Let's cut through the "nD BIM" marketing fluff. For practical purposes in 2025, 3D, 4D, and 5D are the dimensions that bring tangible value to projects daily. Beyond that, while you'll hear terms like 6D (sustainability) or 7D (facility management), these are generally about enriching the existing model with more specific data layers rather than adding fundamentally new dimensions in the same way time and cost do.
3D BIM: The Spatial Foundation
This is your bread and butter – the geometric model. It’s crucial for visualization, spatial coordination, and, importantly, clash detection. Catching that pipe hitting a duct in the model is a lot cheaper and less embarrassing than finding it on site. But in 2025, a standalone 3D model is just the starting point.
4D BIM: Adding the Pulse of Time
This is where things get dynamic. 4D BIM integrates the 3D model with the project schedule. You're essentially linking model elements to tasks and timelines. This allows for powerful construction sequencing visualization. Imagine watching your building assemble itself on screen, phase by phase. This isn't just a neat animation; it helps identify potential logistical bottlenecks, optimize site activities, and communicate the construction plan effectively to all stakeholders. If a delivery is delayed, you can see the ripple effect through the project timeline directly within the model context.
.webp)
Visualizing construction sequencing with 4D BIM helps in identifying potential delays.
5D BIM: Connecting to the Bottom Line – Cost
Now we're talking money. 5D BIM integrates cost information with your 4D model. Every element in the BIM can have associated cost data – materials, labor, equipment. This enables automated quantity takeoffs directly from the model, which are far more accurate and faster than manual methods. More importantly, it allows for real-time cost tracking and forecasting. Change a material specification in the model, and the budget updates. Track progress on site, and you can compare actual costs against planned expenditure. This provides invaluable financial oversight and helps keep projects on budget. That argument about whether a change order is justified? 5D BIM often provides the clear data to settle it.
5D BIM provides dynamic cost estimation linked directly to model elements.
Beyond 5D: Data Enrichment, Not New Dimensions
When you hear about 6D (often cited for sustainability or lifecycle aspects) or 7D (facility management, operations & maintenance), it's generally more accurate to think of these as adding specific datasets or attributes to the existing 3D/4D/5D model. For example, embedding CO2 emission data for materials (sustainability) or warranty information and maintenance schedules for equipment (facility management) into BIM objects is incredibly valuable. However, it doesn't fundamentally alter the dimensional framework in the way time and cost do. The key is enriching the "I" in BIM with relevant, structured data for specific purposes throughout the asset's lifecycle, keeping the core model efficient and focused.
Digital Twins & The Golden Thread: Data That Lives and Breathes
Two terms you'll hear constantly in the 2025 BIM landscape are "Digital Twin" and "Golden Thread of Information." They aren't just buzzwords; they represent a fundamental shift in how we manage building information throughout its entire lifecycle.
The Digital Twin: Your Building's Live Avatar
A Digital Twin is a dynamic, virtual representation of a physical asset – like your building, bridge, or plant. Unlike a static BIM model that's primarily used during design and construction, a digital twin is continuously updated with real-time data from sensors, IoT devices, operational systems, and user feedback. Think of it as the BIM model that "grows up" and gets a job after construction is complete.
It's a living, breathing counterpart that mirrors the actual performance and condition of the physical structure. This allows owners and operators to:
- Monitor performance in real-time (e.g., energy consumption, equipment status).
- Conduct predictive maintenance (e.g., identify a pump that's likely to fail soon based on sensor data).
- Simulate "what-if" scenarios (e.g., the impact of a different operational strategy on energy use).
- Optimize operations for efficiency and occupant comfort.
The BIM model, with its rich geometric and asset data, often forms the foundational layer of a digital twin.
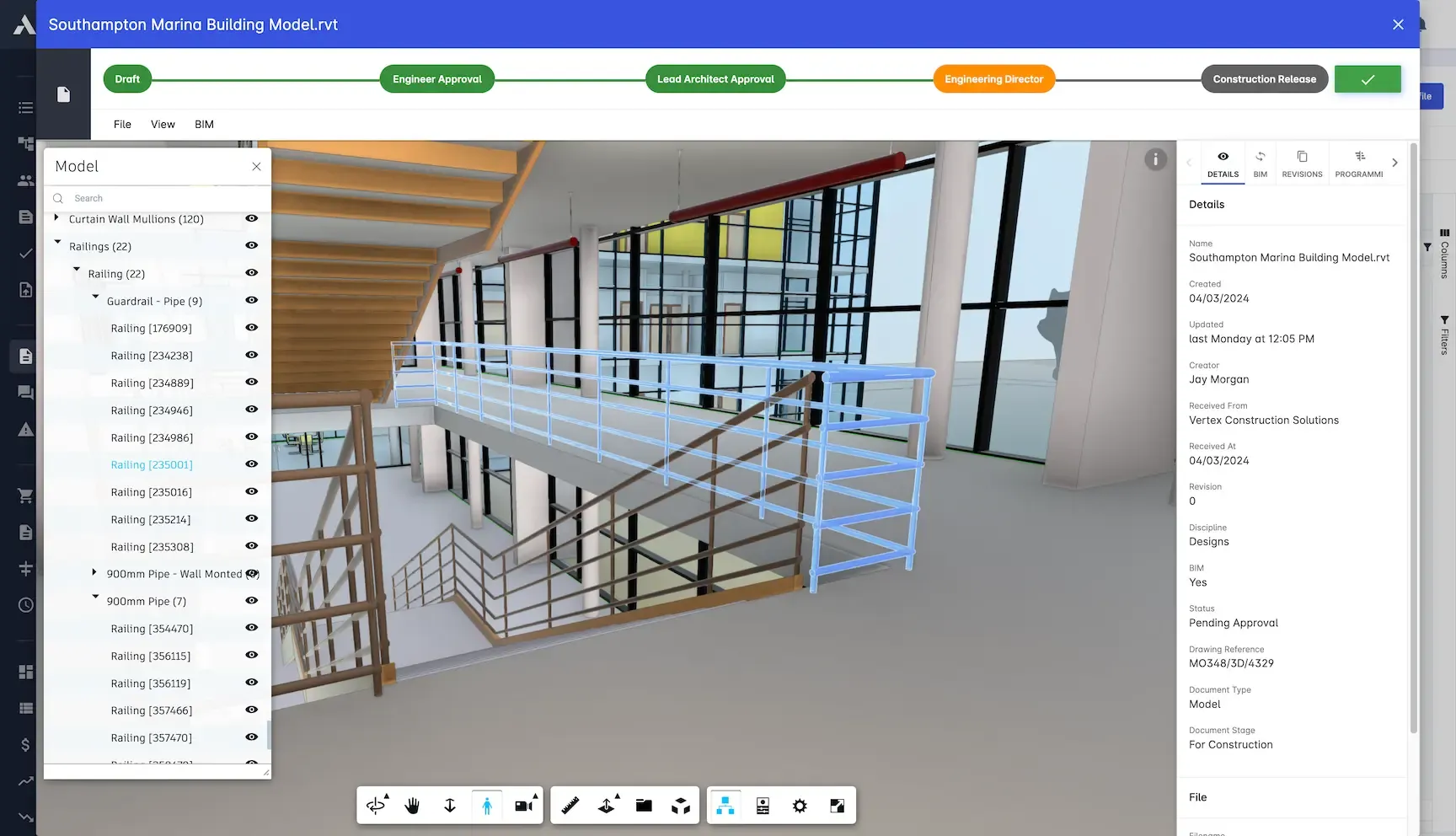
A Digital Twin creates a dynamic link between the physical asset and its data-rich virtual replica.
The Golden Thread: An Unbroken Chain of Truth
The "Golden Thread of Information" is a UK-driven concept that has gained global traction, especially concerning building safety. It refers to the need to have accurate, easily accessible, and up-to-date building information throughout the asset's lifecycle – from initial design concept through construction, occupation, and eventual decommissioning. It's about creating a single source of truth that is maintained and owned.
This isn't just about having lots of data; it's about having the *right* data, structured correctly, and managed diligently. The Grenfell Tower tragedy in the UK starkly highlighted the devastating consequences of poor information management. The Golden Thread aims to ensure that critical information – like fire safety strategies, materials used, and changes made over time – is documented, auditable, and available to those who need it, when they need it. This is vital for safety, compliance, and accountability. A robust BIM process is fundamental to establishing and maintaining this Golden Thread.
Visualizing the BIM Ecosystem in 2025
The BIM landscape of 2025 is a complex interplay of data, processes, and technologies. To better understand these connections, the following mindmap illustrates the core components and their relationships, showing how 3D models evolve with data enrichment, enabling advanced applications like Digital Twins and adherence to concepts like the Golden Thread, all supported by technologies such as AI and cloud platforms.
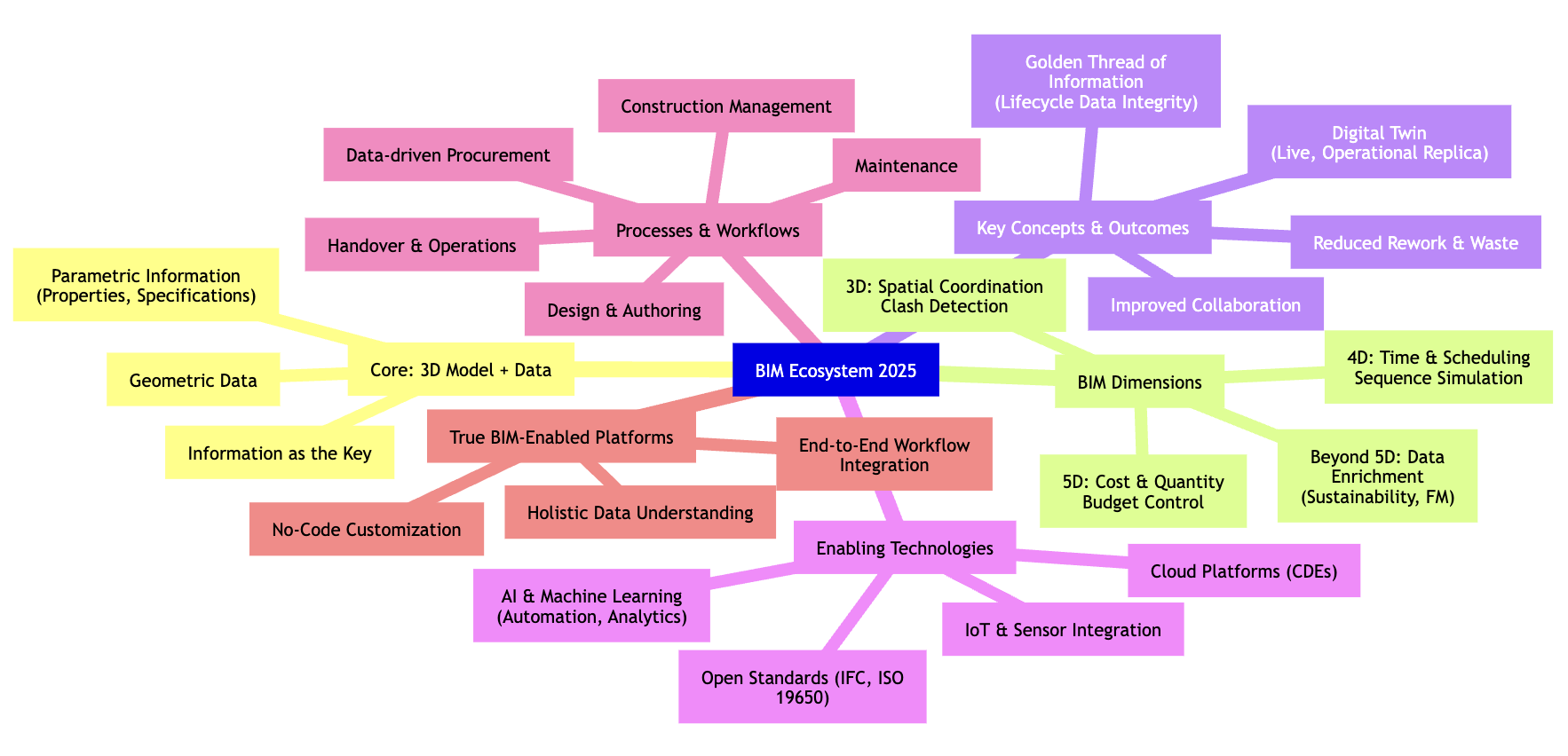
This mindmap highlights how the initial 3D model is just the beginning. Its true power unfolds when enriched with data and extended through dimensions like 4D and 5D, supported by modern technologies to deliver significant outcomes like operational Digital Twins and a reliable Golden Thread of Information, all orchestrated ideally by truly BIM-enabled platforms.
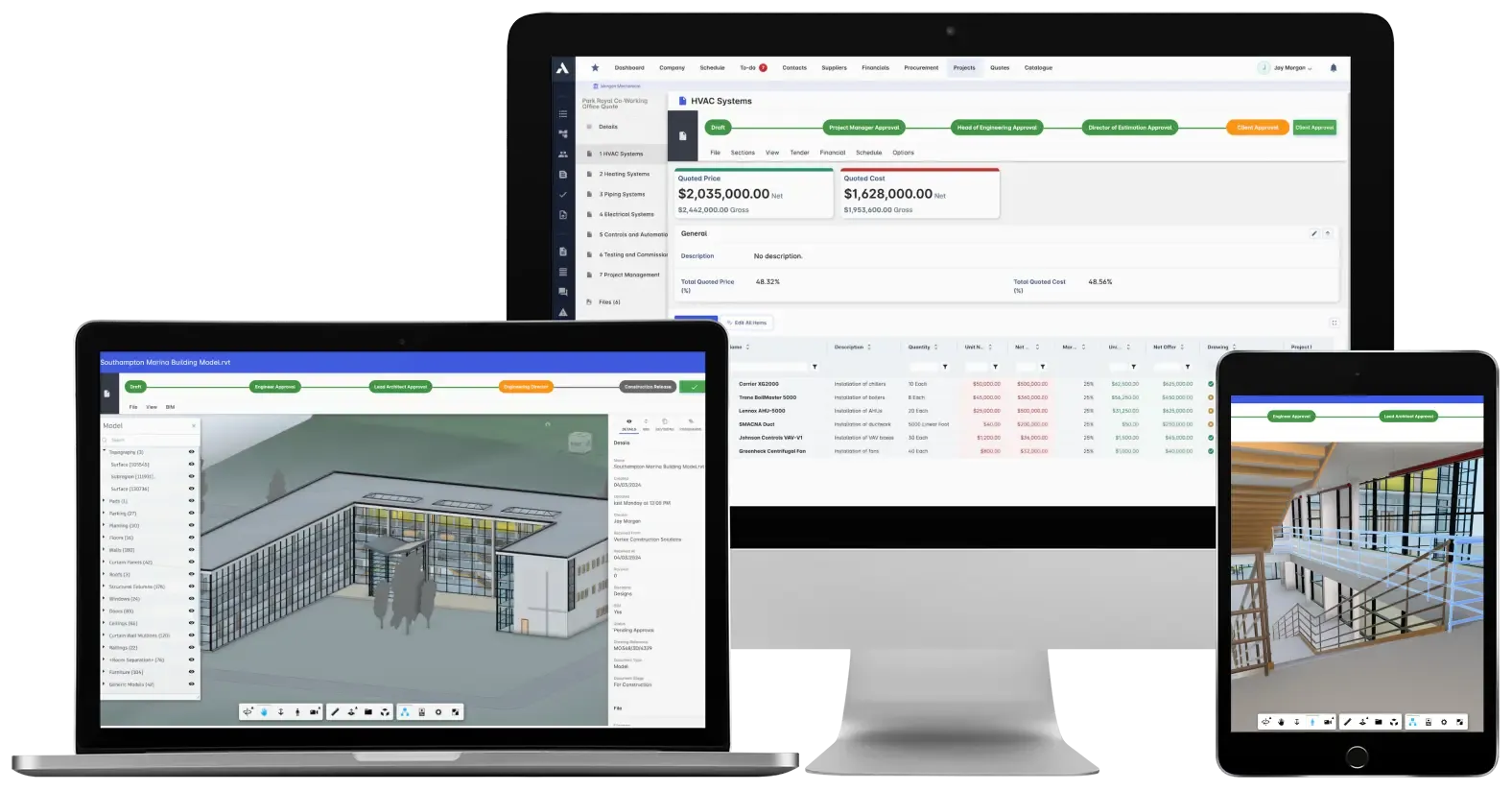
Archdesk: A Genuinely BIM-Enabled Platform
Now, let's talk about what a "true BIM-enabled platform" looks like in 2025, and Archdesk is a prime example. It's not about just importing a 3D model for viewing. It's about fundamentally understanding and leveraging the parametric data embedded within that model to drive holistic project workflows – from design intent right through to handover and even ongoing asset maintenance, effectively functioning as a digital twin's core.
Understanding Data Parameterization: The Archdesk Approach
Archdesk gets that BIM is data-first. The platform is engineered to interpret and utilize the rich parameters associated with BIM objects. For instance, a window object in your BIM model isn't just a pretty rectangle; it carries crucial data:
- Cost Code: Linking it to the correct budget within the overall project structure.
- Dimensions: Exact height, width, depth.
- Specifications: Material type, glazing U-value, acoustic rating.
- Compliance Requirements: Such as a specific fire-rating (e.g., FD60).
Archdesk can extract this granular information directly from the model. This isn't just about display; it's about making this data actionable.
Transforming 3D Data into Actionable Workflows
Here’s how Archdesk puts this parametric data to work, moving beyond what many point solutions offer:
Quantification and Specifications
The platform transforms the 3D BIM data into accurate quantifications and detailed specifications. This forms the bedrock for subsequent processes. No more manual takeoffs or re-entering data into separate spreadsheets, which is where errors often creep in.
RFQ Processes and Procurement
The extracted specifications (like that fire-rated window) directly populate Request for Quotation (RFQ) packages. This ensures suppliers are quoting based on the exact design intent captured in the BIM model. The procurement process becomes data-driven and transparent.
Subcontractor Agreements with Built-in Compliance
This is where it gets really smart. Archdesk can use specific parameters from the BIM model – like the "fire-rating" of a door or window – to enforce compliance in subcontractor agreements. For example, if the model specifies an FD60 fire-rated door set, Archdesk can be configured to ensure that only subcontractors with the necessary certifications to install FD60 doors can be assigned that work package. If you, as the main contractor, requested Archdesk to check this specific certification based on the model data, the platform's no-code engine allows this customization. This direct link from model parameter to contractual compliance is a massive step up from manual checks and significantly reduces risk. It's like having an automated compliance officer working off your BIM model.
Payment Applications and Invoices Tied to BIM Objects
When contractors submit applications for payment or invoices, these can be directly linked to the specific BIM objects they've worked on. This provides unparalleled clarity in tracking progress and validating payments against the model.
Rendering Progress Back in 3D
Archdesk doesn't just pull data out; it can also push information back. Progress of work, inspection statuses, and other data points collected during construction can be visualized directly on the 3D model. Imagine color-coding elements based on their installation status or inspection results – a powerful visual tool for project meetings and status reporting.
The No-Code Engine: Powering Custom, Data-Driven Workflows
A key enabler for this deep integration is Archdesk's no-code engine. This allows project teams to customize workflows and automate processes based on BIM data without needing to write complex code. This flexibility means the platform can adapt to specific project requirements and company procedures, making the BIM data work exactly how you need it to.
The Holistic Vision: What BIM Was Meant For
This end-to-end, data-centric approach is what BIM was always intended to achieve. Instead of fragmented "point solutions" that require manual data transfer and often lead to information silos, Archdesk provides a cohesive environment where BIM data flows through the entire project lifecycle. From initial design and quantification, through procurement, construction management, financial controls, and finally to handover and even serving as the data backbone for a digital twin in the operational phase for asset maintenance, the information remains consistent and connected. This is a far cry from just using BIM for clash detection and then shelving the model.
AI in BIM: Making Data Even Smarter
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept in construction; by 2025, it's actively enhancing BIM processes, making them more efficient and insightful. One of the key areas AI is making a difference is in "vectorizing data" alongside its parameters.
Vectorizing Data: Giving Structure to the Unstructured
In simple terms, vectorizing data involves converting information, often from raster images (like scanned 2D drawings or site photos) or point clouds, into structured vector graphics. More importantly in the BIM context, it's about AI algorithms not just creating lines and shapes, but also intelligently identifying objects within that data and associating them with relevant parameters (e.g., identifying a wall and inferring its likely material type or dimensions based on visual cues and project context).
This is powerful because it allows BIM systems to ingest and understand data from sources that were previously difficult to integrate. AI can help:
- Automate the conversion of legacy 2D drawings into preliminary 3D BIM models with basic parameters.
- Process point cloud data from laser scans or drone photogrammetry to create as-built models, with AI identifying and classifying elements like pipes, ducts, or structural members.
- Infer missing parameters or validate existing ones by comparing model data with site photos or other documentation.
Other AI Applications Enhancing BIM:
- Advanced Clash Detection: AI can go beyond simple geometric clashes, learning from past projects to identify more complex or discipline-specific conflicts, and reducing false positives. Someone probably wishes they had that on that one hospital job...
- Generative Design: AI algorithms can explore thousands of design options based on predefined goals and constraints (e.g., optimizing for structural efficiency, energy performance, or cost), presenting designers with a range of viable solutions.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical project data and real-time information from BIM models and IoT sensors, AI can help predict potential risks, such as schedule delays, cost overruns, or safety hazards, allowing for proactive intervention.
- Automated Code Compliance Checking: AI tools are emerging that can analyze BIM models against building codes and regulations, flagging potential non-compliance issues much earlier in the design process.
- Intelligent Quantity Takeoffs: AI can assist in more accurate and context-aware quantity takeoffs, understanding nuances that simple object counting might miss.
The integration of AI makes BIM not just a repository of data, but an intelligent system capable of analysis, prediction, and automation, ultimately helping project teams make better decisions faster.
BIM Capabilities Radar: A Comparative Snapshot
To illustrate how different platforms might stack up in the 2025 BIM landscape, this radar chart offers an opinionated comparison across several key capability areas. This isn't exhaustive, but gives a sense of where strengths might lie for platforms like Archdesk when compared to some other well-known solutions. The scores are illustrative, based on the functionalities discussed and industry trends.
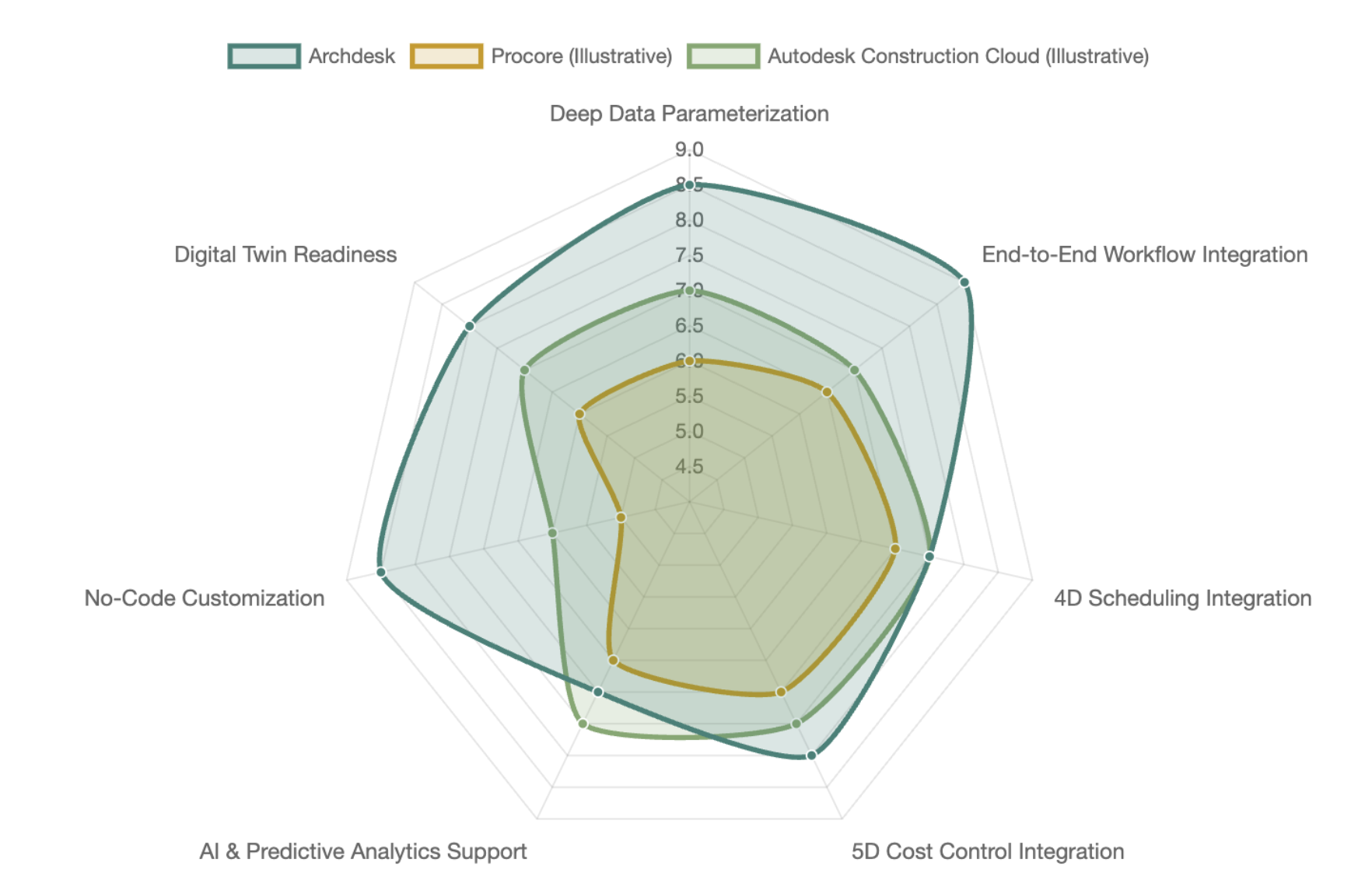
This chart suggests that while many platforms offer strong features in specific areas, a platform like Archdesk aims for a more balanced and deeply integrated approach, particularly excelling in how it handles BIM data parameterization and allows for no-code workflow customization to truly leverage that data across the project lifecycle.
BIM in Action: US & UK Company Examples
Theory is great, but let's look at how companies are applying these advanced BIM practices in the US and UK. While specific internal workflow details are often proprietary, we can see the impact on major projects and the types of services being offered.
United Kingdom: Driven by Mandates and Megaprojects
The UK has long been a proponent of BIM, with government mandates (like BIM Level 2, and now the UK BIM Framework evolving towards more integrated data environments) pushing adoption.
- Major Infrastructure Projects: Projects like Crossrail and HS2 have been significant proving grounds for BIM, utilizing it extensively for design coordination, 4D scheduling, and managing vast amounts of project data. The focus on a "Golden Thread" of information is particularly strong here.
- Tier 1 Contractors (e.g., Balfour Beatty, Skanska UK, BAM Construct): These firms have embedded BIM into their standard practices. They leverage BIM for clash detection, 4D/5D modeling, site logistics planning, and increasingly, for creating digital records that feed into operational phases. Skanska UK, for instance, has showcased its use of 5D BIM for better cost control on complex projects.
- Consultancies (e.g., Arup, Mott MacDonald): These global firms, with strong UK presence, use BIM for complex design analysis, sustainability assessments, and developing digital twin strategies for clients. Arup's work on projects often involves sophisticated data management and simulation using BIM models.
The UK's push for BIM Level 3 compliance concepts, emphasizing better information management and interoperability (ISO 19650), continues to drive sophistication. There's a strong emphasis on creating structured data that can be used throughout the asset lifecycle.
United States: Growth Through Efficiency and Innovation
The US BIM market is characterized by strong private sector adoption and increasing use in public infrastructure projects.
- Large General Contractors (e.g., Skanska USA, Mortenson, Turner Construction): These companies utilize BIM extensively for pre-construction services, clash detection, 4D scheduling, and virtual design and construction (VDC). Mortenson, for example, has been noted for its innovative use of BIM and digital technologies, including piloting digital twin concepts for progress tracking. Skanska USA also employs BIM for improved project visualization and coordination on large-scale projects like hospitals.
- Specialized BIM Service Providers (e.g., Tesla Outsourcing Services): Companies like these offer a range of BIM services, from model creation and clash detection to 4D/5D simulation and BIM consulting for clients across various sectors.
- Engineering Firms (e.g., Jacobs Engineering, HDR Inc.): These firms use BIM for complex infrastructure design, integrating GIS data, and performing sophisticated analyses. They are increasingly involved in developing digital asset management strategies for their clients.
While federal mandates aren't as overarching as in the UK, many state and local government agencies are requiring BIM on public projects, driving adoption. The focus is often on leveraging BIM for improved efficiency, reduced rework, and better collaboration.
BIM Platform Capabilities: A Comparative Glance
When evaluating BIM platforms in 2025, it's useful to compare them across key capabilities that reflect true BIM enablement. The following table provides a high-level comparison of Archdesk with some other known platforms in the construction technology space. This is based on generally understood strengths and how they align with the data-centric BIM approach discussed.
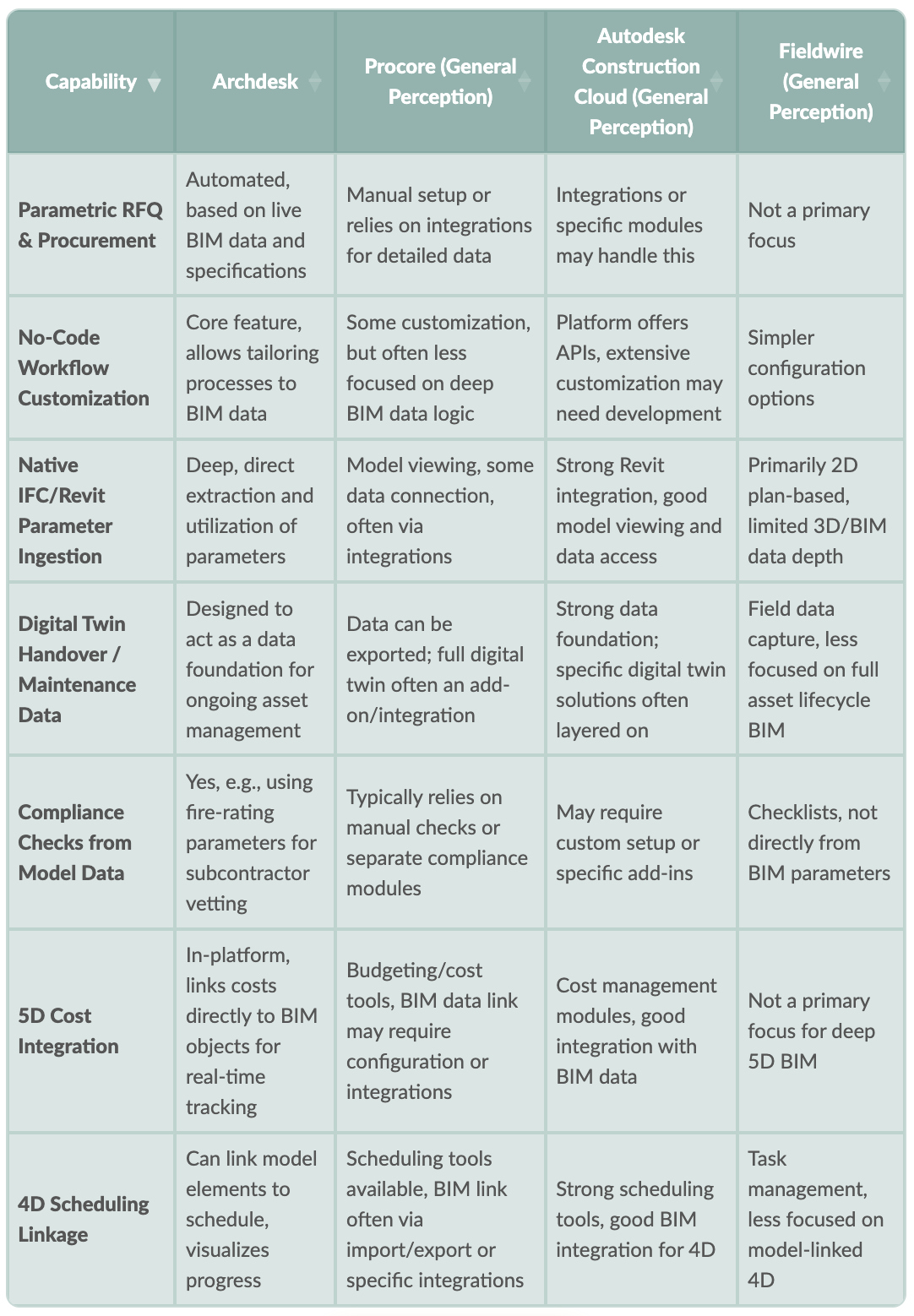
Note: This table reflects general capabilities and common use cases. Specific features can vary based on product versions, modules, and integrations. "General Perception" indicates a common understanding rather than a definitive statement on all possible configurations.
The key takeaway here is the difference in approach. While many platforms can interact with BIM data, platforms like Archdesk are built to fundamentally operate on that data, using its inherent intelligence to drive a wider range of connected workflows with greater native cohesion.
Frequently Asked Questions (for the BIM Savvy)
How does 'vectorizing data' with AI actually improve my day-to-day BIM tasks?
Think about getting a bunch of old 2D scans for a renovation project. Manually redrawing them into BIM and adding all the parameters is a slog. AI-powered vectorization can automate a chunk of this by recognizing elements like walls or doors, converting them to vector objects, and even inferring basic parameters (like "this is likely an internal wall"). This means less donkey work for you, faster model creation from existing docs, and a better starting point for detailed modeling. It also helps in processing point clouds from as-built surveys, turning raw scan data into more usable, object-oriented BIM elements rather than just a dumb mesh.
Is the 'Golden Thread of Information' just a UK regulatory headache, or is it relevant globally?
While the specific term "Golden Thread" and its legislative backing are prominent in the UK (largely post-Grenfell), the underlying principle is globally critical. Every project, anywhere, benefits from accurate, accessible, and maintained information throughout its lifecycle. Think of major project failures or safety incidents worldwide – poor information management is almost always a contributing factor. So, while you might not have a "Golden Thread mandate" in your region, adopting its principles (clear data ownership, structured information, change control, accessibility) is just good practice for risk management, efficiency, and delivering safer, better-performing assets. BIM is a core enabler for this, regardless of geography.
Beyond 5D, what's the most practical 'data enrichment' I should focus on for real project benefits?
It really depends on your project type and client needs, but two areas offer big practical wins:
- Facility Management (FM) / Operational Data: Embedding information like manufacturer, model number, warranty expiry, maintenance schedule, and spare parts for key equipment (HVAC, pumps, lifts etc.) directly into BIM objects. This makes handover to the client far more valuable and sets the stage for efficient operations and maintenance. This is often what's vaguely termed "7D BIM."
- Sustainability Data: Incorporating parameters related to environmental performance, such as embodied carbon of materials, recycled content, operational energy predictions, or LEED/BREEAM credit information. As sustainability becomes non-negotiable, having this data in your BIM model helps in making informed design choices and demonstrating performance. This is often linked to "6D BIM."
Focus on data that solves real problems for the client or asset owner post-construction.
My company uses several different software tools. How can a "holistic" BIM platform truly simplify things without forcing us to abandon everything else?
A truly holistic BIM platform, especially one built on open standards (like IFC), doesn't necessarily demand you abandon all specialist tools. Instead, it aims to be the central nervous system for your project data. It should excel at ingesting data from various sources (e.g., design authoring tools via IFC, scheduling software, estimating packages) and, crucially, *making sense of that data* to drive integrated workflows within its own environment for things like procurement, cost control, and progress tracking. The value comes from reducing manual data re-entry, ensuring consistency, and providing a single source of truth for key project aspects. It's less about replacing every tool and more about becoming the intelligent hub that connects and leverages the data from them, particularly the rich data from your BIM models.
References
- Archdesk BIM Integration - Archdesk.com
- Common Data Environment - Archdesk.com
- BIM Trends to Watch in 2025 - RDT Technology
- Top BIM Companies in the USA for 2025 - Vocal.media
- The Future of BIM: Trends to Watch in 2025 - Taaltech.com
- Leveraging the Updated UK BIM Framework: A Guide for 2025 - GlobalCAD.co.uk





