The Construction Industry Scheme (CIS) aims to streamline taxation resulting from the working relationship between contractors and subcontractors.
By having a clear understanding of CIS tax deductions, you can save yourself penalties worth £100-£3000 due to non-compliance.
In this guide, we explain the Construction Industry Scheme and answer frequently asked questions about its implementation and benefits for the construction sector.
What is the Construction Industry (CIS) Scheme?
The Construction Industry Scheme requires contractors to deduct tax at source from the payments made to self-employed companies or subcontractors for their construction services.
Contractors must pay the tax deducted to the HMRC by the 22nd of every month in accordance with the subcontractor's tax status - that is, 20% of the gross payment for registered subcontractors and 30% for non-registered subcontractors.
Subcontractors can reclaim CIS refunds with their National Insurance contributions and their year-end tax deductions.
Read this article if you want construction software to help with CIS and other accounting processes.
Why was the Construction Industry Scheme started?
The Construction Industry Scheme helps stop tax avoidance and makes it easy for self-employed subcontractors to pay their income tax on time.
For this, they leveraged their clients ( the contractors) by placing an obligation on them to carry out the tax deductions.
CIS scheme results in subcontractors paying advance tax and National Insurance for the tax year.
Any non-compliance leads to penalties for both a contractor and subcontractor.
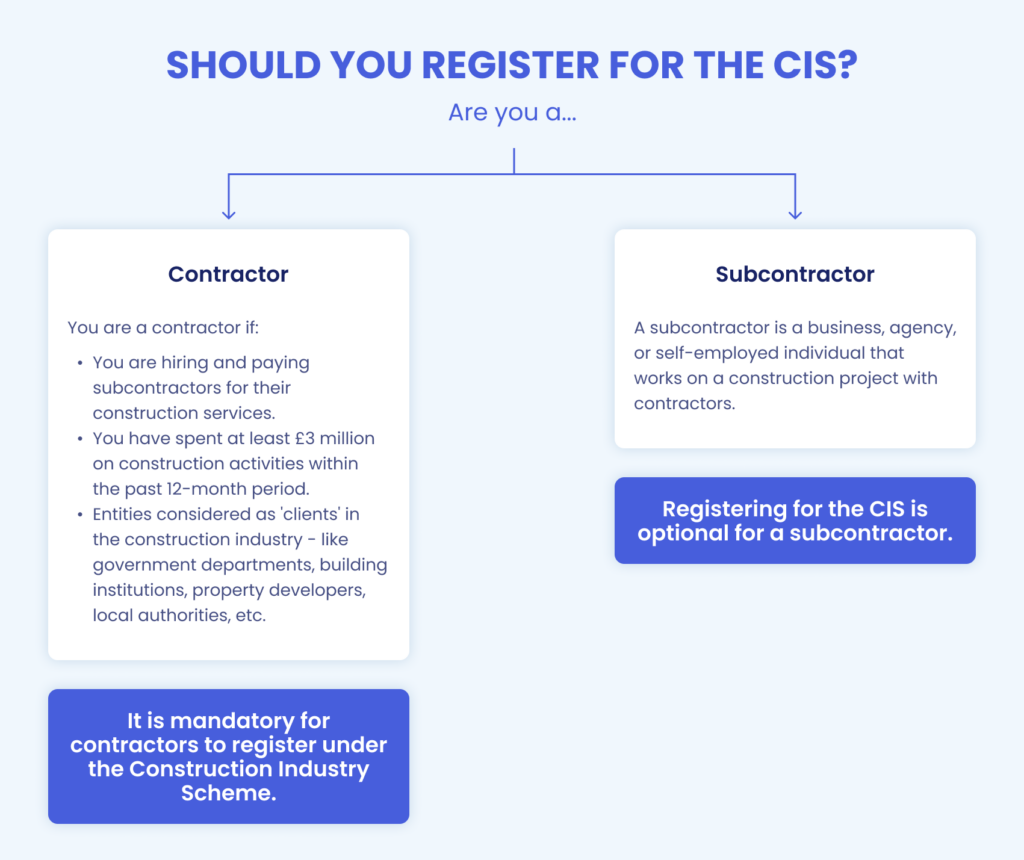
Should you register for the CIS?
CIS covers all kinds of businesses in the construction industry across limited companies, self-employed individuals, sole traders, and partnerships.
Who is considered a contractor?
You are a contractor if:
- You are hiring and paying subcontractors for their construction services.
- You have spent at least £3 million on construction activities within the past 12-month period.
- Entities considered as 'clients' in the construction industry - like government departments, building institutions, property developers, local authorities, etc.
Construction activities by private residents are not considered under the CIS tax.
Furthermore, a contractor can be a deemed contractor or a mainstream contractor.
Mainstream contractors include property developers, foreign businesses that undertake construction activities within the UK or gang leaders who organise construction labour for any construction project.
Deemed contractors include non-construction businesses that undertake construction work like oil companies, housing associations, public offices, government development corporations, etc.
Note:
It is mandatory for contractors to register under the Construction Industry Scheme.
Check out this essential guide to accounting in construction.
Who is considered a subcontractor?
A subcontractor is a business, agency, or self-employed individual that works on a construction project with contractors.
On successful delivery, they receive payment outside the PAYE scheme.
Note:
Registering for the CIS is optional for a subcontractor.
On registration, a contractor must deduct 20% tax on the payment, while non-registered ones face a tax deduction of 30%.
Also, public bodies and local authorities who are subcontractors need not apply for registration. Instead, they are registered for gross payment status.
What if you are both a contractor and a subcontractor?
Sometimes, a business is undertaking subcontracting activities, such as civil engineering work, while also working as a subcontractor for other construction businesses.
In this case, you must follow compliance and taxation procedures separately as a contractor and a subcontractor.
Is there a difference between UK and non-resident contractors/subcontractors?
The contractor scheme is concerned with construction work carried out within defined UK territories.
This is irrespective of the nationality of both a contractor and subcontractor, payment location, or mode of payment.
However, a subcontractor has to register with HMRC before starting the construction work within UK territories.
For this, a company, whether they are hiring subcontractors in the UK or taking up construction work as subcontractors, must register with the Specialist Personal Tax office.
Learn more about how companies with various employment statuses can register with CIS.
You can also contact HMRC to raise your corporation tax enquiries and get the necessary guidance.
[H1] What works fall under the CIS?
The CIS scheme applies to every activity undertaken by the construction industry in the United Kingdom and its offshore territorial waters up to a limit of 12 miles.
This is applicable irrespective of whether the business is UK-based or not. However, any construction operations or civil engineering work carried out outside the UK is not accountable to this scheme.
Broadly, this scheme applies to the following construction expenses carried out on any property:
- that is an investment
- is available for sale or rent
- is not used for their business purpose, but is allowed for commercial usage by a third party
The following construction services and works carried out on permanent or temporary structures are eligible under the CIS tax scheme:
- Site landscaping
- Site demolitions and dismantling
- Site preparations
- Site alterations
- Site construction
- Repairs and finishing for construction sites
- Internal and external site decorations and cleaning
- Installation of systems
What work is exempt from the CIS?
Certain jobs not considered construction operations are as follows:
- Activities that involve only the delivery of construction materials
- Manufacturing of systems or construction components like air conditioners, machinery, lighting, etc.
- Preparing signboards
- Any artistic work or installations
- Drilling and extraction of natural resources
- Professional work like architect consultations, surveying land, etc.
- Construction work carried out on your property.
Any construction work carried out on nursing homes, charity organisations, warehouses, education authorities, own offices or leased property is exempted from the scheme.
Deemed contractors are exempt from the scheme for small construction operations or contracts that cost less than £1000, excluding the cost of materials incurred.
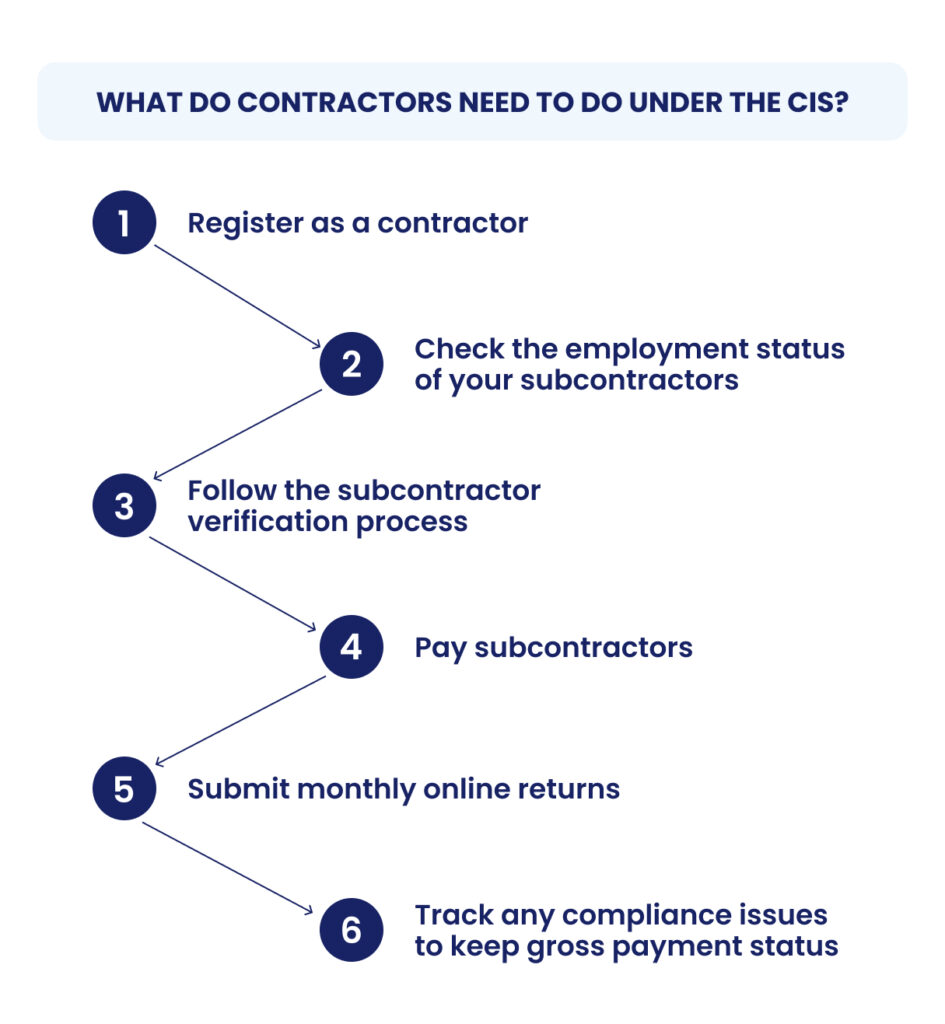
What do contractors need to do under the CIS?
Here's the procedure a contractor must follow under the Construction Industry Scheme (CIS):
Step-1: Register as a contractor
Entities that identify as a contractor must register with Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs (HMRC) as an employer. This registration process should be completed before paying subcontractors.
You will require a Government Gateway User ID, password, National Insurance Number, business name, and UTR for the employer registration.
In about 15 working days, you will receive the employer PAYE reference number.
Here's the link to register online as an employer based on your business status:
- Click here to register online if you are a limited company with 1-9 directors
- Click here to register for other business types
Step-2: Check the employment status of your subcontractors:
Know your hired subcontractors' details to gain clarity on their employment status - are they employed by an agency, an independent business, or self-employed?
Knowing employment status is necessary because the CIS tax is applicable for labour that identifies itself as a subcontractor. If they are employees, then you have to define payroll to deduct PAYE and National Insurance Contributions.
Step-3: Follow the subcontractor verification process
Is your subcontractor registered with HMRC?
You can conduct the subcontractor verification process online on the official website - Construction Industry Scheme online service or use commercial CIS software.
Ensure you keep the following details as a contractor available to you:
- Contractor entity name
- Address
- Contact details
- Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR)
- Accounts office reference
- Employer reference number
- Construction contract details as agreed upon with the subcontractors
You need to keep the following subcontractors' details ready as per their employment status:
Limited company subcontractors:
- Company name
- Company Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR)
- Company registration number
Partner in a company:
- Company registration number OR UTR
Individual partners:
- Partner's National Insurance Number or UTR
Partner in a firm:
- Partner's name
- Name of the firm
- Firm's Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR)
Sole trader:
- Sole trader UTR
- Sole trader name
- Sole trader National Insurance Number
You have to consult HMRC to confirm your subcontractor's tax status. HMRC will let you know if your subcontractor has gross payment status or net payments.
They will also provide you with a verification number and rate to deduct tax on future payments.
Doing this is necessary, especially when you are engaging in a construction contract with the subcontractor for the first time.
Once you obtain the verification number and tax rate, you can continue with future payments without repeat verification - provided you included the subcontractor in your returns in the current or 2 prior tax years.
What does the 'unmatched' response by HMRC mean?
If HMRC comes with an 'unmatched' response, it means either the subcontractor has not registered with the sub-contractor scheme or their identification information might be incorrect.
What if there is a change from Gross Payment to payment under CIS deductions?
HMRC will inform both a contractor and subcontractor with a 90 days notice about any changes in the payment process as per Gross Payment or with CIS deductions.
Till then, the contractor should continue to pay subcontractors in the same way as per the prior verification status until further notice by HMRC.
Step-4: Pay subcontractors
HMRC will instruct the contractor on how to pay subcontractors based on the verification and employment status as follows:
- Gross Payments: you have to pay for the construction work with 0% tax deducted
- Tax deducted with standard rate: if your subcontractor is registered with HMRC, you have to deduct tax at 20% of the payment
- Tax deducted with a higher rate: if your subcontractor is not registered with HMRC or is unverifiable by HMRC, then you have to deduct tax at 30% of the payment.
A contractor can make their CIS deductions payments like how they make for National insurance contributions or PAYE.
You can learn more about how these payments are done for better understanding - Guide to employers' PAYE
Note:
A contractor should deduct the tax from the amount that excludes any material cost payments that the contractor incurs.
Include plant hire costs like cement mixers, scaffolding, cranes, pumps, etc., and fuel required for its operations as material costs.
Contractors can refer to Appendix D of the Construction Industry Scheme explainer to understand how to determine material costs.
Also, the amount on which the deduction is made should include any travel or fuel expenses incurred by the subcontractor.
Step-5: Submit monthly online returns
CIS contractors must file online monthly returns for all payments that are done to subcontractors irrespective of CIS deductions - Monthly returns online service portal
File the returns by the 19th of each month or by 14 days before the tax month end.
For example, if your tax month was from 7 September to 6th October - you must provide your payment statement by 19th October.
A contractor can choose how to submit the payment and deduction statements, but they must include the below-mentioned aspects:
- Contractor details: Name and employer tax reference
- Subcontractor details: Name and UTR
- Amount: gross payment made to the subcontractor
- Material costs: total amount excluded as material costs
- Final payment statement: the total amount of withholding tax and final payment made to the subcontractor
- VAT paid: total VAT the subcontractor has charged
Note:
You do not have to file nil returns in the event of no payment to subcontractors
Also, there is no option to file employer annual returns.
Step-6: Track any compliance issues to keep gross payment status
Any regular failure to submit payment statements, deduction statements, or paying subcontractors will attract penalties.
This includes reconsideration of the gross payment status of the contractor or subcontractor.
Also, ensure you do not commit errors in your payment submission, as HMRC takes serious action for intent or negligence-based cases.
Frequent negligence-based errors can hamper your gross payment status if you are both a contractor and subcontractor.
You must contact the HRMC (via CIS Helpline) to inform them about any underpayment, advance payments, overpaid tax, or incorrect returns filed for any construction work.
HMRC will help you confirm the next steps to fix the issue.
For approved defaults by HMRC, you can make changes in the CIS online service portal and update your returns accordingly.
You have to select the 'Returns' menu, and then click on the 'Amend Return' option.
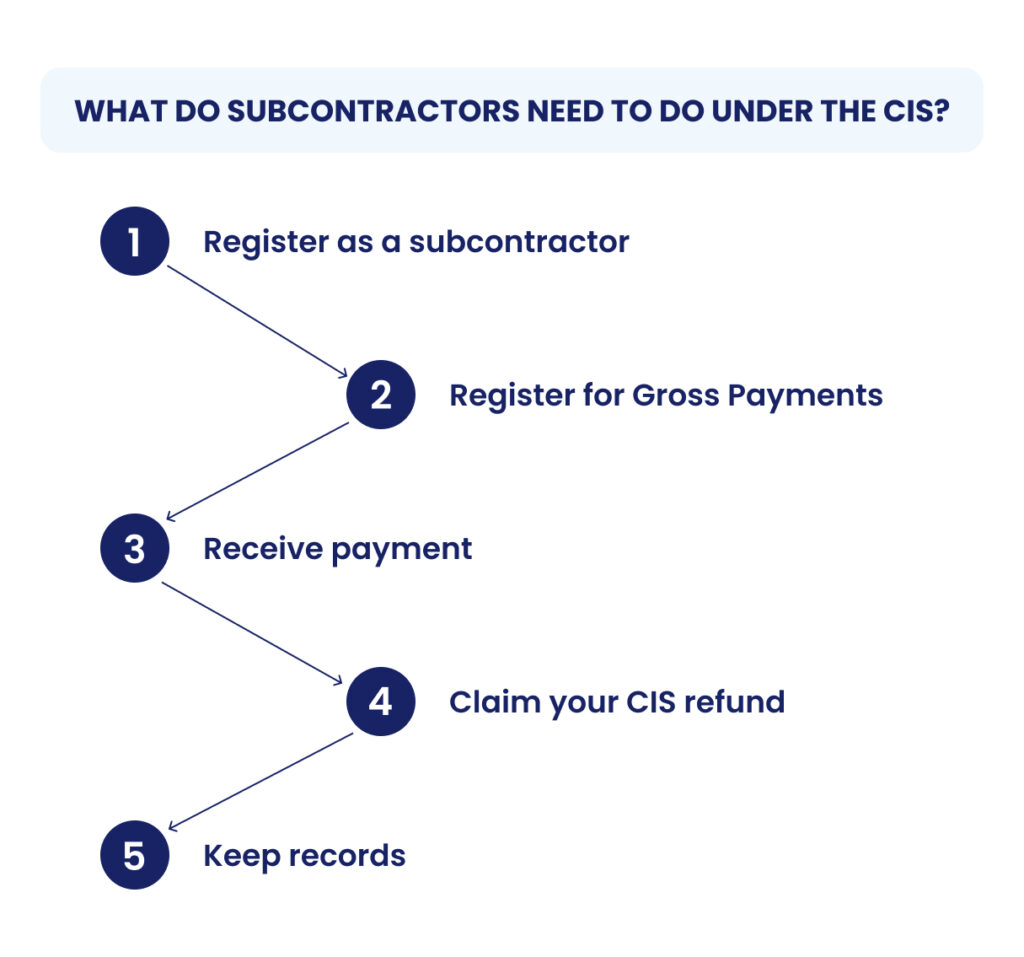
What Do Subcontractors Need to Do Under the CIS?
Here is the step-by-step procedure a subcontractor must follow under the Construction Industry Scheme (CIS):
Step 1: Register as a Subcontractor (not mandatory, but beneficial)
Registering with HMRC as a subcontractor means you have to pay 10% less tax deduction for the construction work carried out.
For this, you must clarify your employment status as a subcontractor.
Here's how you can register as a subcontractor based on your employment status:
Sole Trader or Self-Employed:
Find your Unique Taxpayer Reference number.
If you don't have one, then take up self-assessment to get your UTR as a self-employed - Register for self-assessment.
Please note, you require a mandatory Government Gateway User ID and password for taking up the self-assessment - Sign in to Government Gateway.
Within 10 working days, you will receive your UTR number by mail and sooner on the HMRC app. This signs you up for both CIS and self-assessment.
Partnerships or Limited Company Subcontractors:
By 5th October at the end of the tax year, you need to register for self-assessment if you are a partner in a partnership firm - Register for self-assessment.
You must have your UTR number available.
Also, ensure you are already registered as a:
- limited liability partnership
- limited company,
- trust, depending on your company structure.
Non-self-employed Individuals:
You must register online or by post for self-assessment by 5th October 2023 after the end of the tax year, if you need to complete a tax return for April 2022 - April 2023.
You need to use form SA1 for registration.
Then, within 10 working days, you will receive your UTR by mail or on the HMRC app.
As per the Construction Industry Scheme, here's how your tax deduction will take place:
- If you register as a subcontractor: your contractor has to deduct 20% from your construction work payments and submit them to HMRC.
- If you do not register as a subcontractor: your contractor will deduct 30% from your construction work payments.
- If you have gross payment status: your contractor need not deduct any amount.
These tax deductions are considered advance payments for your income tax and National Insurance Contributions.
Do Subcontractors Outside the UK Have to Register for the Construction Industry Scheme?
The CIS scheme applies to non-resident subcontractors working in the UK territories.
Step 2: Register for Gross Payments
What is the 'Gross Payment' Status?
If you become eligible for gross payments, it means construction businesses pay you the complete amount agreed upon for the construction work without any tax deductions.
This also means that you have to pay your income tax and National Insurance by the end of the tax year.
How Can Subcontractors Apply for Gross Payment?
You can apply to become eligible for gross payments while registering for the Construction Industry Scheme in 3 simple steps:
- Log in to the Government Gateway using your Government Gateway User ID and password.
- Select 'Other Services' from the 'Tax Account' menu.
- Select ‘Construction Industry Scheme – Subcontractors’ and proceed with the instructions.
If you have already registered for the CIS scheme, then you can call the CIS Helpline and fill up the relevant form as per your employment status.
Here are the links to the forms:
- Sole Trader: [Form link]
- Partnership: [Form link]
- Limited Company: [Form link]
How Can Subcontractors Qualify for Gross Payment Status?
To qualify for gross payment status, subcontractors must follow these steps:
HMRC conducts compliance tests on your construction business to determine eligibility for gross payment status.
These tests include:
- Timely income tax and National Insurance payments for the previous tax year
- Conducting construction work within defined UK territories
- Having a valid bank account
For the previous 12 months, your construction business must meet the following turnover requirements (excluding VAT):
- At least £30,000 for sole traders
- At least £30,000 per partner for partnerships
- At least £30,000 per director for limited companies
For partnership firms or limited companies, the total turnover must be at least £100,000 (excluding VAT) for the previous 12 months.
Step-3: Receive payment
As a subcontractor, you must cooperate with your contractor to ensure error-free verification, tax deduction, and bank account payments.
We have listed the details a contractor will require from you in the Step-3 verification process of the 'What do subcontractors need to do under the CIS?' section.
For calculating the tax deduction amount, the following aspects will NOT be considered:
- VAT
- Plant hire and fuel costs for its operation
- Material costs
Completing the verification procedure is essential to ensure correct CIS deductions.
If a contractor is unable to verify you due to incorrect information or incomplete CIS registrations, you will face a 30% deduction.
Step-4: Claim your CIS refund
Your contractor will submit payment statements for the tax month for your construction work.
Using this, your accountant needs to determine any income tax or National Insurance you must pay to HMRC.
Depending on your business type, you need to file the return at the tax year-end as follows:
- Partner and sole trader: Complete the self-assessment to record your invoices and CIS deductions.
HMRC will determine pending tax and National Insurance bills along with paying your CIS refunds.
You have to pay the remaining amount before 31st January for the tax year. - Limited company: You need to file a Corporation Tax return if you have gross payment status.
If you pay CIS tax, then you need to share the Full Payment Submission and Employer Payment Summary with HMRC.
Based on this, HMRC will determine the remaining PAYE income tax and National Insurance that you must pay before the due date.
Step-5: Keep records
HMRC expects you to keep records of the payments and CIS refunds made, for which, you can use form CIS132.
For subcontractors with gross payment status, HMRC will perform an annual review of your construction business to check eligibility.
Any non-eligibility is explained by HMRC and can be appealed to by you.
If you undergo any business change in your employment status, add a shareholder, shut down the company, or change your business name or address - you must inform HMRC via the CIS helpline.
Example of How the CIS Deductions Work
Let us understand the CIS deductions under 3 separate conditions:
Example 1: Registered subcontractor supplies only labour and no materials
- Labour costs for construction work: £500
- Tax deduction: 20%
- Amount of tax deducted to HMRC: £100
- The total amount paid to the subcontractor: £400
If the subcontractor is not registered, then the deduction would be 30% at £150.
Payment statement on contractor's tax month return:
- Total payment for construction work: £500
- Materials cost: £0
- Tax deducted: £100
Example 2: Registered subcontractor supplies both labour and materials
- Labour costs for construction work (labour costs): £500
- Material cost incurred by subcontractor: £50 + £50 VAT = £100 (Note: if the subcontractor is registered for VAT, you need not add £50 to your calculations)
- Plant hire and fuel costs: £100
- Total amount invoiced to the contractor: £500 + £100 + £100 = £700
- Tax deduction rate: 20%
- Amount of tax deducted to HMRC: 0.2*(£700 - £100) = £120 (Note: here, the contractor calculates the deduction post excluding the material costs)
- The total amount paid to subcontractor: £580
If the subcontractor is not registered, then the deduction would be 30% at £180.
Payment statement on contractor's tax month return:
- Total payment for construction work: £700
- Materials cost: £100
- Tax deducted: £120

Example of Payment and Deduction Statements
Below is a screenshot of an example payment and deduction statement shared on the official guide:
Keeping Payment Statements Record and the Key Payment Submission Dates to HMRC
HMRC expects contractors to keep payment statement records.
It accepts both online and scanned payment statements of the original document as long as it is unaltered and legible.
For this, HMRC has the following requirements from contractors with regards to payment submission records:
- Post-tax year end, keep the records for a minimum of 3 years
- Ensure the records are available when requested by HMRC
- Ensure view access to the records
- Provide record copies when requested by HMRC
What are the key dates for CIS tax deductions?
For each tax month, irrespective of the withholding tax rates or deductions, contractors should pay subcontractors within 14 days of the month's end.
Be mindful of the time it may take you to process payments within key payment statement submission dates.
Not paying on time or the correct amount will result in penalties as discussed in the next section.
How to Avoid Penalties, Fines, and Appeals
HMRC conducts regular contractor record inspections to ensure construction industry contractors are fulfilling their obligations. The inspection procedure is the same as how HMRC inspects employees' PAYE records.
Types of Offences and Penalties
Based on your offence, HMRC will take the following action:
False declarations
- Penalty: Fine of £3,000
- If you submit any false documentation or false payment statements to HMRC for availing gross payment status, then HMRC will impose fines on you.
Contractors who do not operate the CIS deductions scheme correctly
- Penalty: gross payment status cancellation
- Any misuse of the Construction Industry Scheme via frequent errors in payment submissions will result in revoking the status of gross pay for the contractor.
Filing late returns for the tax month
- Penalty: £100 - £300 depending on the number of months in delay
- Filing late returns for the tax month makes you responsible to pay late fees as follows:
- less than 2 months post-filing date: penalty of £100
- 2 months post-filing date: penalty of £200
- 6 months post-filing date: penalty of £300 or 5% of deductions - whichever is greater
- 12 months post-filing date: penalty of £300 or 5% of deductions - whichever is greater
Failing to inform about no return
- The contractor must inform HMRC about no subcontractors' pay being due in the previous tax month by the 19th of the month. In case you are keeping your engagement with the subcontractor for the construction project on pause, then HMRC will mark 'inactive' to their CIS tax scheme.
- Failure to do so results in a penalty.
Incorrect monthly return
- HMRC charges penalties on the contractor if they believe you incorrectly filed a return with intention or negligence.
- The following scenarios are covered under 'incorrect' return filing:
- entering the incorrect amount of paid tax
- incorrect verification number or employment status declaration
- not correctly conducting the verification process and employment status checks
- omission of subcontractor or payments on the return filed
Missing deduction statements or records
- Penalty: £3,000
- If HMRC asks to share the records, and if the contractor fails to provide them on time or shares incorrect information, they will face a penalty of £3,000.
Do I Need to Hire a Specialist to Help with the CIS Requirements?
CIS software is available in the market to help with compliance. Software like Archdesk can help you manage your CIS processes.
Although, hiring a specialist can help you stay accountable, organised, and avoid mistakes that result in penalties from HMRC.
You can consider hiring a specialist to manage CIS deductions in the below scenarios:
- If you identify both as a contractor and subcontractor, a specialist will ensure you remain compliant amidst frequent transactions.
- If you work with many subcontractors having varied employment statuses and you need someone to manage them.
- If you are working with a non-UK resident contractor or subcontractor, then you may need the help of an expert due to the complexities involved.
Note:
- Conduct thorough research on the professional you choose to work with to avoid any unscrupulous activities.
- Some professionals may charge based on a percentage of claims, and that would result in them inflating invoices. Ensure you or your agent does not adopt such practices else you may face penalties from HMRC under false declarations.
Stay Compliant with the Construction Industry Scheme
You can learn more about the CIS tax and access the CIS portal from the Business Tax section of the UK Government website - Business Tax.
HMRC also conducts regular webinars that explain various nuances of the CIS scheme. You can access them here - HMRC webinars.
If you have more questions, then you can contact the CIS Helpline or access their community forum for quick resolutions.
Steady cooperation between contractor and subcontractor is the first step to avoid any penalties or hassle with the HMRC. Make construction work documentation, clean accounting, record maintenance, and timely payments a part of your business workflows for efficient taxation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What if a subcontractor is not registered for CIS?
A contractor deducts 20% from a registered subcontractor's payments as advance tax to HMRC on your behalf. If a subcontractor is not CIS registered, then they will face a 30% tax deduction instead.
Is CIS exempt from IR35?
As per HMRC's point 47, IR35 or off-payroll tax rules take precedence over the Construction Industry Scheme (CIS). You must audit construction labour hired and check employment status to determine any obligations under IR35 or CIS.
What is the point of CIS?
CIS ensures efficient and timely taxation for subcontractors and contractors carrying out construction operations in the UK territories. Its aim is to prevent any tax fraud or evasion.
Depending on the CIS registration tax status of the subcontractor, a contractor deducts 20% or 30% of the payments and submits them to HMRC as advance tax.
Do subcontractors have to pay VAT?
If your subcontractor is VAT registered, then contractors need not account for VAT in their deduction statements.
Learn more about VAT reverse charges from this webinar by HMRC - How to apply the VAT reverse charge for construction services.
How long does it take to become CIS registered?
If you do not have a UTR number, you have to register for the same, which usually takes 10 working days. You can contact the CIS Helpline to enquire about your application status and seek guidance.
How do I get a refund of overpaid tax under the Construction Industry Scheme (CIS)?
If you paid more tax and national insurance, you can claim online or by post. Your claim should include the company name, address, contact, UTR, PAYE reference numbers, and an estimation of the overpaid amount. You can also choose to deduct the overpaid tax amount with your VAT, Corporation tax, or other liabilities.
Do agents who manage subcontractors need to register under CIS?
If you are managing the subcontractors for the construction work, you need to register as a contractor under CIS. If you are merely connecting the contractor with subcontractors, and are not involved in the construction operations, then you need not register under CIS, but your client contractor needs to.
When was the Construction Industry Scheme launched?
The CIS tax scheme came into effect in 1971 to ensure the construction industry was not participating in any tax evasion activities.
Is CIS Calculated on Labour Only?
CIS is calculated only on labour delivered for the construction operations. It excludes any material costs that the subcontractors incur.
Due to this, contractors need to verify the accuracy of material costs to ensure a subcontractor does not inflate their material costs to save CIS tax deductions. Additionally, HMRC may inspect the invoices by asking for relevant bills on construction material expenses.
Does CIS Apply to Domestic Work?
The CIS scheme does not apply to any construction project that involves homeowners or domestic work. In this case, homeowners will pay subcontractors the complete amount without any deductions.
It is the responsibility of the subcontractor to pay the relevant income tax at the year's end.
Does CIS Expire?
CIS registrations do not expire. However, if you have gross payment status, HMRC will conduct necessary renewal procedures to ensure you still comply with their gross payment criteria.
How Do I Know If My Company Is CIS Registered?
You can contact HMRC via the CIS Helpline to enquire about your CIS registration status.





